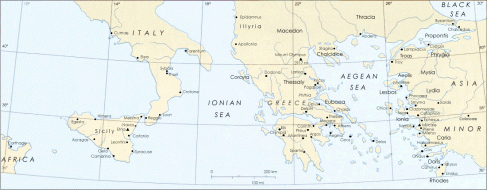
Ancient Greece is located in Southern Europe, on the southern end of the Balkan Peninsula. The surrounding countries of ancient Greece were Italy, Illyria, Thrace and Asia Minor.
Mainland Greece is mountainous land almost completely surrounded by Mediterranean Sea. Greece has more that 1400 islands.
MAP OF ANCIENT GREECE AND SURROUNDING COUNTRIES
The country consists of a large mainland; the Peloponnese, a peninsula connected to the southern tip of the mainland by the Isthmus of Corinth; and a large number of islands, including Crete, Rhodes, Corfu, the Dodecanese and the Cyclades.
The country ranges approximately in latitude from 35°00′N to 42°00′N and in longitude from 19°00′E to 28°30′E. As a result, it has considerable climatic variation.
Today, Greece is surrounded on the north by Bulgaria (former Thrace), the Republic of Macedonia (former Yugoslavia) and Albania (former Illyria); to the west by the Ionian Sea; to the south by the Mediterranean Sea and to the east by the Aegean Sea and Turkey (former Asia Minor). Ancient Thrace corresponds to an area that today would cover Southern Bulgaria, North Eastern Greece and European Turkey.

MAP OF GREECE TODAY AND SURROUNDING COUNTRIES
BIBLIOGRAPHY
- Chisholm, J. (et al). (n.d.). The Usborne Encyclopedia of Ancient Greece. London. Usborne Publishing.
- http://plato-dialogues.org/tools/gk_wrld.htm. Last accessed 15 May 2012.
- http://www.ancientgreece.co.uk/. Last accessed 15 May 2012.
- http://www.nationsonline.org/oneworld/map/greece_map2.htm. Last accessed 15 May 2012.